ISO 18192-3: Implants for surgery – Wear of total intervertebral spinal disc prostheses – Part 3: Impingement-wear testing and corresponding environmental conditions for test of lumbar and cervical prostheses
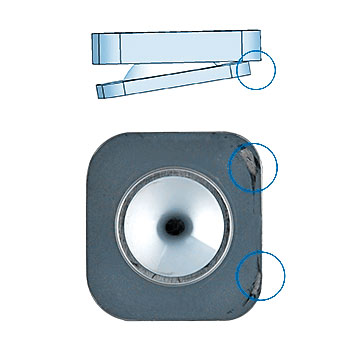
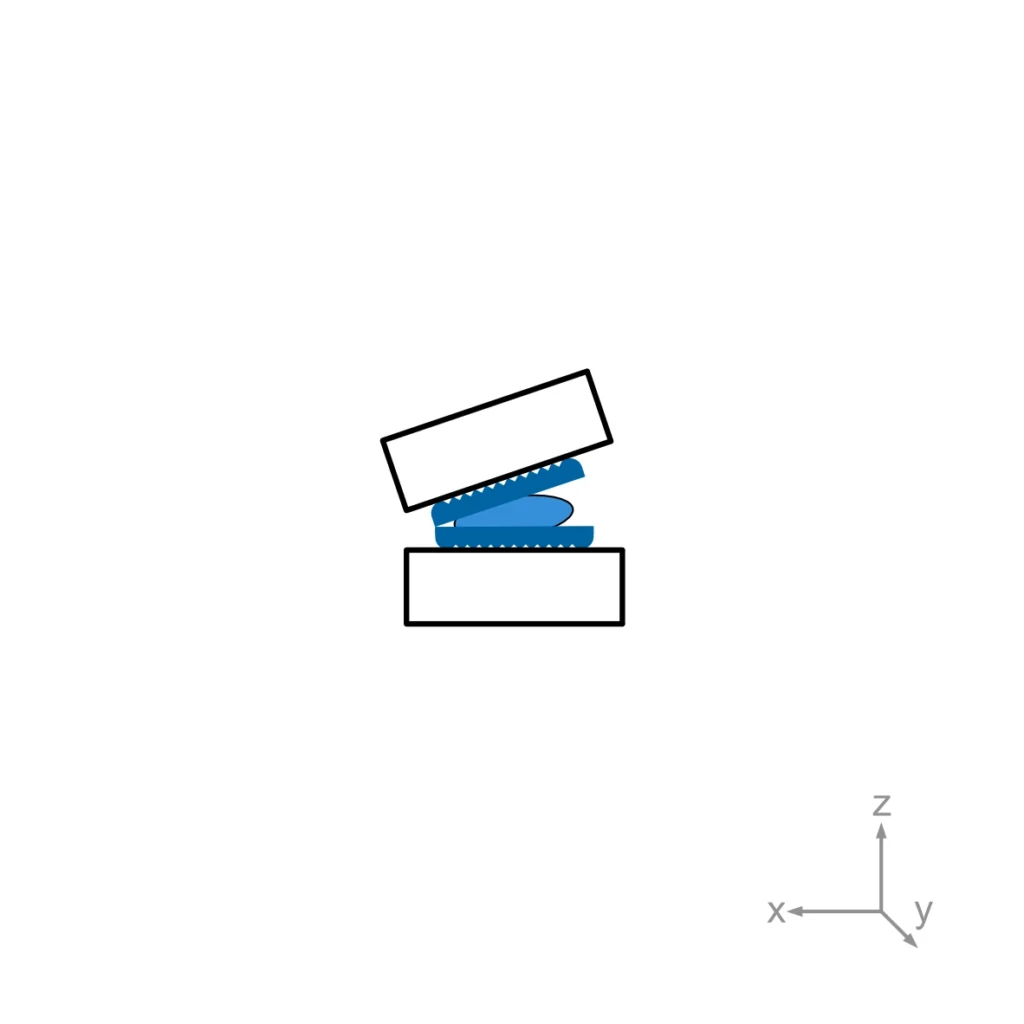
This test method covers a procedure to simulate impingement between the inferior and superior endplate in a spinal disc prosthesis; the subsequent assessment of wear; and assessment of contact pattern.
The EndoLab® spine simulator is used for this type of testing. An axial load and a time-varying angular displacement are applied to the lumbar prostheses. The axial load remains constant during impingement and fluctuates in a sinusoidal waveform during the remaining movement. Thus, a constant moment is applied during impingement.
The specimens are inspected after 125 thousand, 250 thousand, 500 thousand and after 1 million cycles. At each inspection, the wear of the prostheses is determined by gravimetric measurements.
SEM of the bearing surfaces as well as particle analysis can be performed.