ISO 18192-2: Implants for surgery – Wear of total spinal intervertebral disc prostheses – Part 2: Nucleus replacements
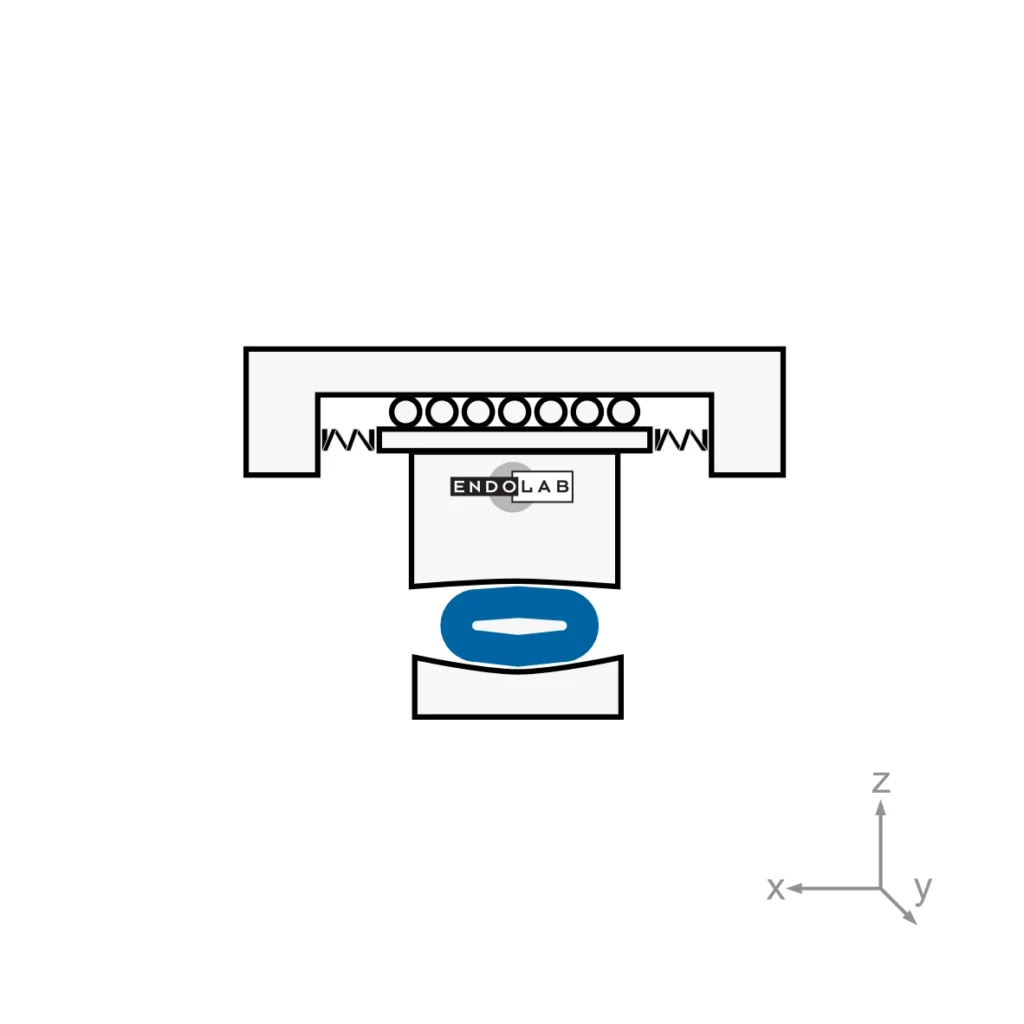
This International Standard defines a test procedure for the relative angular movement between articulating components and specifies the pattern of the applied force, speed and duration of testing, sample configuration and test environment to be used for the wear testing of spinal nucleus prostheses.
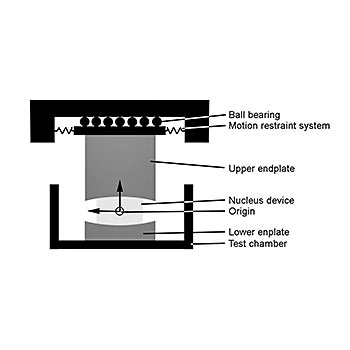
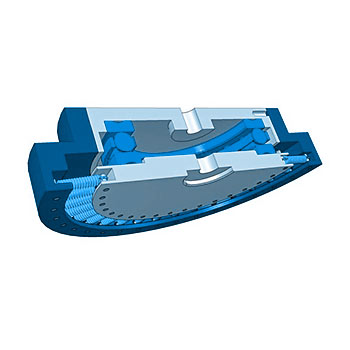
Three moving axes as well as one computer controlled dynamic loading axis are used to simulate the in-vivo conditions. The shear stiffness of the annulus is simulated by a motion restraint system. All tests are performed under newborn calf serum diluted with deionized water with a resulting protein content of 20g/l. In general, six specimens plus two soak controls are tested simultaneously. The amount of wear is determined by weight loss of the specimens according to ISO 14242-2. The test is stopped after 10 million cycles.
SEM of the bearing surfaces as well as particle analysis can be performed.