ISO 7206-4: Implants for surgery – Partial and total hip joint prostheses – Part 4: Determination of endurance properties and performance of stemmed femoral components
ISO 7206-6: Implants for surgery – Partial and total hip joint prostheses – Part 6: Endurance properties testing and performance requirements of neck region of stemmed femoral components
PI-58 (ISO 7206-8): Implants for surgery – Partial and total hip joint prostheses – Part 8: Endurance performance of stemmed femoral components
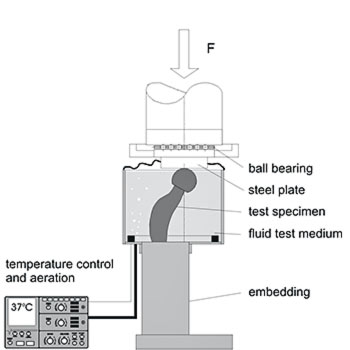
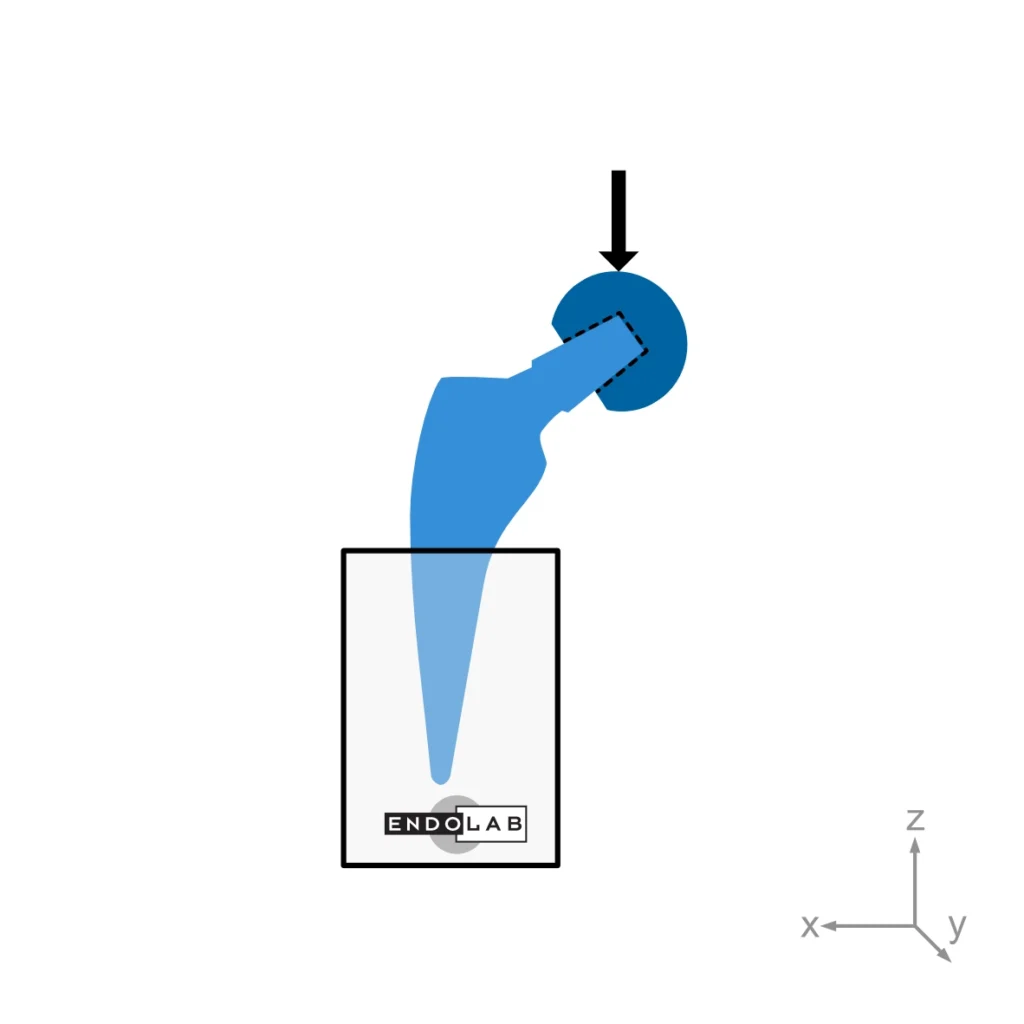
The fatigue test according to ISO 7206-4 simulates the dynamic loading of a hip stem during gait. Proximal loosening of the stem is presumed to simulate worst case conditions and replicates clinical failure. Load inclination, embedding level, load level and number of cycles are given by the test standard. The test conditions do provide safety information about fatigue failure of hip stems by a simplified model.
ISO 7206-6 simulates a well ingrown stem. Fracture (if any) is expected to occur at the neck region of the stem.
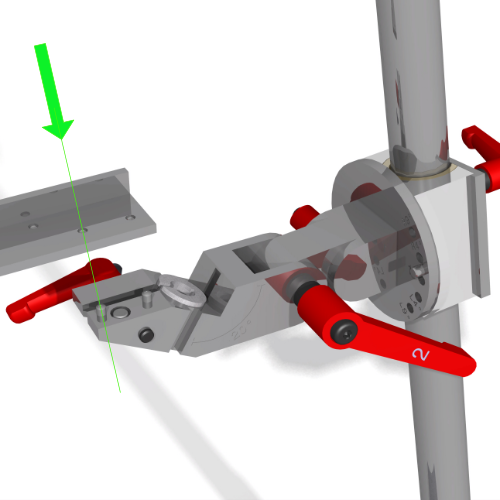
The alignment of the hip stem versus the test load is straightforward for simple hip stem geometries but may be challenging for anatomic stems. EndoLab® has developed a 3D CAD based method to design custom AM-printed jigs for sample alignment.
The maximum test frequency depends on the flexibility of the stem and the performance of the test equipment. EndoLab® developed special tools to embed the stem correctly (see Fig.) which ensure constant loading of the implant. Most of our tests are performed using MTS® or Zwick® test equipment.