ISO 14242-1: Implants for surgery – wear of total hip prostheses – Part 1: Loading and displacement parameters for wear-testing machines and corresponding environmental conditions for tests
ISO 14242-2: Implants for surgery – wear of total hip prostheses – Part 2: Methods of measurement
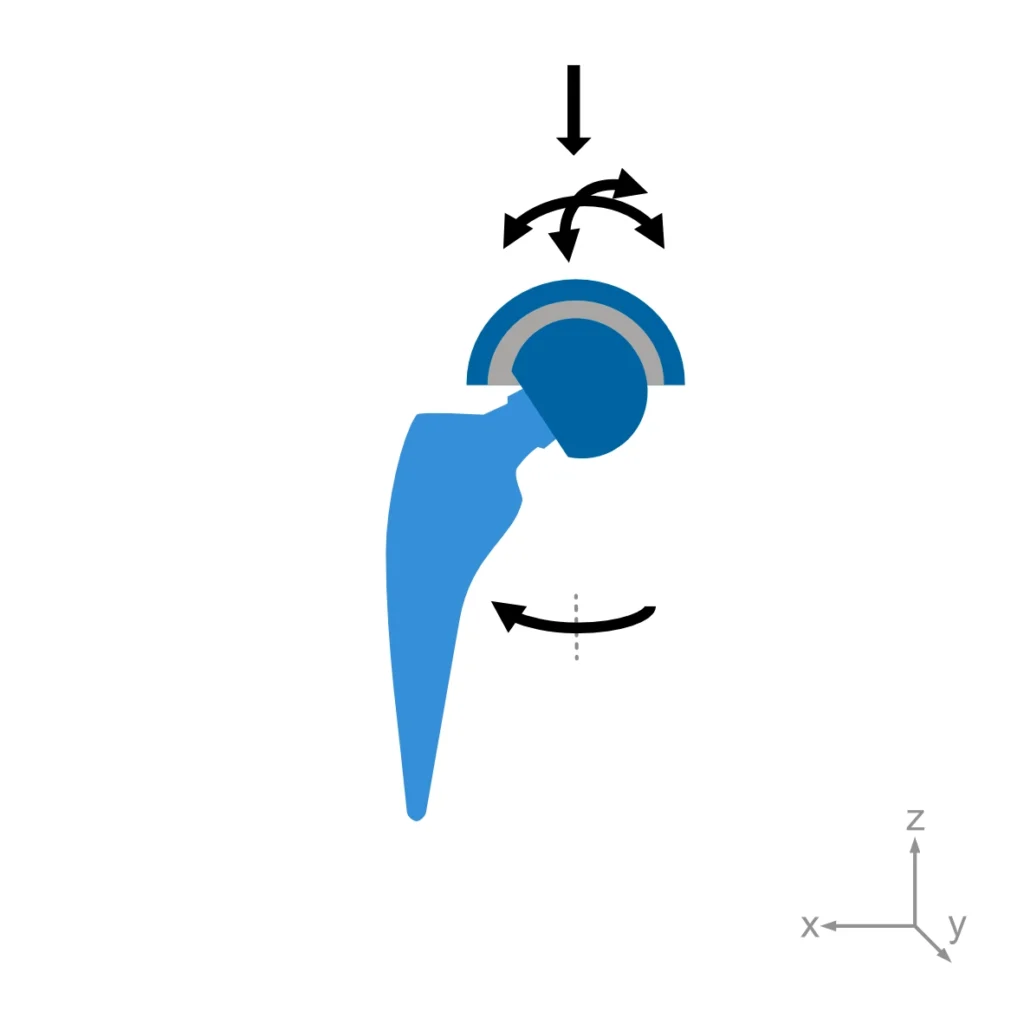
The hip joint simulator developed and built at EndoLab® can test 2×3 specimens simultaneously (plus two soak controls). The specimens are oriented in an anatomically correct position, and the resulting hip joint force is applied via the cup. Consequently, the direction of the force vector is constant relative to the cup and moves relative to the head. All three in-vivo angular displacements are simulated: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction and internal/external rotation.
You can see the simulator moving in this short video.
The specimens are assembled under laminar flow conditions and sealed in capsulated single test chambers to prevent contamination. The test fluid’s temperature and fluid level are controlled continuously throughout testing. The wear of the components is determined gravimetrically.
This test is often combined with preconditioning according to ASTM F2003, analysis of the wear debris according to ISO 17853 as well as ion concentration analysis.
Parameters
| Parameters | ISO 14242 |
| force curve | double-peak according to PAUL |
| force is fixed relative to | cup |
| force maximum | 3.0 kN |
| frequency | 1.0 Hz |
| cup inclination „L“ according to ISO 14242 -1 | 30° (corresponds to an in-vivo inclination of 45°) |
| inclination cup-ball | 0° |
| flexion-extension | +25/-18° |
| abduction-adduction | +7/-4° |
| rotation | +2/-11° |
| test fluid | calf serum |
| temperature | 37°C |
| cycles | 5 million |
| inspection cycles | 0.5 million, 1 million, 2 million etc. |
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information