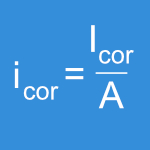ASTM F1875: Standard Practice for Fretting Corrosion Testing of Modular Implant Interfaces: Hip Femoral Head-Bore and Cone Taper Interface
Two methods are part of this standard, a quantitative analysis (method I; long-term evaluation) and a qualitative assessment (method IIb; short-term evaluation).
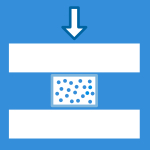
Method I is used to determine the fretting corrosion behavior in the long-term. The interface surface damage and generation of corrosion products are determined through optical evaluation (micro- and macroscopic, SEM/EDX) and particle and ion concentration analyses of the test solution after cyclic loading.
Method IIb is a short-term electrochemical evaluation (current measurement) to compare different designs and surface treatments. This requires extremely precise testing equipment and a well-shielded test environment.
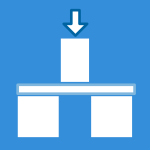
This standard defines the testing, analytical, and characterization methods for evaluating the fretting corrosion performance at the bore and cone interface of the head-stem junction in modular hip implants under cyclic loading in a corrosive environment.
Method I = long-term, cyclic loading with fluid analysis and surface characterization to quantify debris/ions and damage.
Method IIb = short-term electrochemical (current measurement) screening under cyclic loading for comparative assessment (for design changes only).
Typically, the long-term method I is expected for submissions. Method IIb is intended to compare design changes. Always confirm with your regulatory authority and submission strategy.
Whenever your THR design includes a modular femoral head–neck junction, and you need evidence on fretting/fretting-corrosion at the taper interface. It’s also referenced within ISO 21535’s normative set.
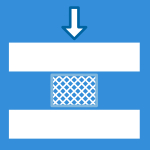
Corrosion, discoloration or debris on the taper surfaces and dulling of machine lines as well as particle and ion release into the test fluid.
Post-Fatigue: Static Disassembly Test according to ISO 7206-10 or ASTM F2009 and particle analysis according to ASTM F1877 and ASTM F561
There is no acceptance criterion defined in the standard. Predicate device testing under the same conditions is recommended.