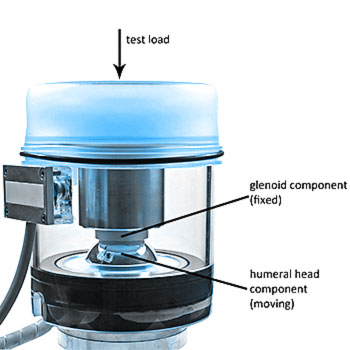
PI-62: Anatomic Shoulder System Wear Test
The test parameters for anatomic shoulder replacement systems are based on a wear study conducted by Wirth et al [1].
A modified EndoLab® hip joint simulator is used for the testing.
The following motions are applied simultaneously to the implant system: Abduction/adduction, flexion/extension, translation within the plane of abduction/adduction, translation within the plane of flexion/extension as well as forward/backward elevation. A constant load of 756 N (± 50 N) is applied. According to Wirth et al. the translation, resulting in rim loading during abduction/adduction is oriented at a 45° angle from the long axis of the glenoid component. The amount of translation required to generate rim loading during abduction/adduction depends on the radial mismatch between the glenoid component and the humeral component and will be adjusted individually. The wear test is conducted for 5 million cycles. The wear is determined gravimetically.
[1] Michael A. Wirth, MD, Conrad Klotz, BS, MBa, Daren L. Deffenbaugh, MS, Don McNulty, MS, PE, Laura Richards, Beng, Joanne L. Tipper, PHD: Cross-linked glenoid prosthesis: A wear comparison to conventional glenoid prosthesis with wear particulate analysis. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (2009) 18, 130-137