ISO 17853: Wear of implant materials – Polymer and metal wear particles – Isolation, characterization and quantification
ASTM F561: Standard Practice for Retrieval and Analysis of Medical Devices, and Associated Tissues and Fluids
ASTM F1877: Standard Practice for Characterization of Particles
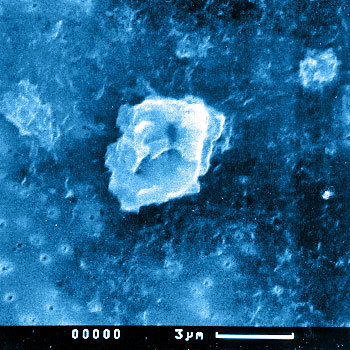
The biological activity of smaller particles is often greater than that of larger particles of the same material. Additionally, the shape of the particles may also play a role in the biological activity. Analyzing particle morphology (size and shape) is therefore crucial for evaluating the long-term stability of joint replacements and other types of implants.
The morphology of the particles can be described using characteristic parameters such as equivalent circle diameter (ECD), aspect ratio (AR), and form factor (FF). These parameters are outlined in ASTM F1877.
When analyzing particles from biological, proteinaceous medium, protein digestion and filtration processes are required before analysis and characterization. ISO 17853 and ASTM F561 offer different methods for digestion and particle isolation suitable for the particles of interest and material sensitivities.
Fluid preparation methods:
- Hydrochloric acid: Many joint replacement devices and implants use UHMWPE and PEEK for bearing materials. These polymers are inert to hydrochloric acid, which is extremely effective at digesting proteins, so the acid digestion method is typically used when these types of materials are of interest.
- Proteinase-k: Most materials, such as metals, some ceramics, and other polymers are not inert to hydrochloric acid. Therefore, a less aggressive, enzymatic digestion method with proteinase-k is used when these types of materials are of interest.
Analysis:
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): Used for imaging the particles on filters or silicon wafers followed by image analysis to determine the morphology and distributions.
- Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX): Used to identify elemental species.
Further analyses:
The EU MDR has identified certain substances which are “…carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic to reproduction (CMR), of category 1A or 1B” (Part 3 of Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council).Many of these substances are metals that are common in alloys used in joint replacement devices. Ion concentration analysis via inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and/or emission spectrometry (ICP-ES) is often used to assess ions released during various implant tests.