Overview
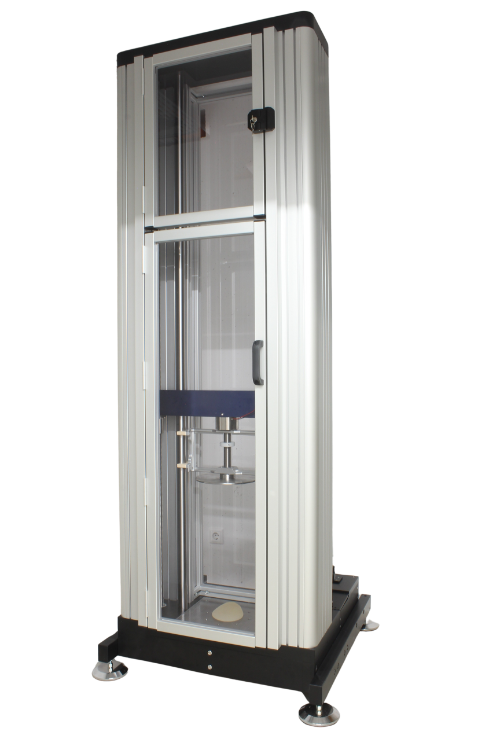
For surgical instrument manufacturers seeking to validate their products against the stresses of clinical use, our automated impaction testing drop tower is essential for qualifying instruments that are repeatedly struck with a hammer or mallet. This includes bone cutting and splitting instruments such as osteotomes, chisels, and gouges used in orthopedic and maxillofacial procedures, where the blade’s integrity and the shaft’s resistance to fracture are paramount.
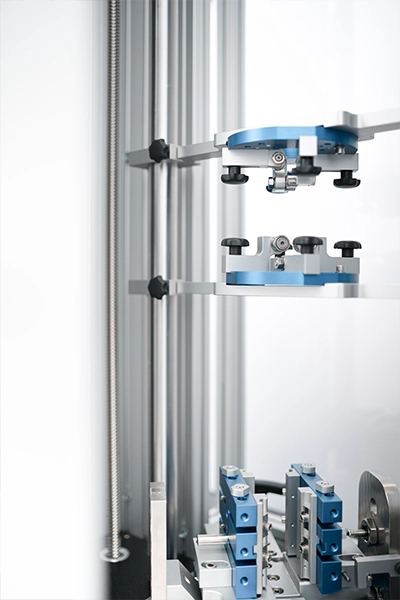
We also test implant driving instruments like impactors and tamps used to seat prosthetic components in arthroplasty to ensure their couplings and strike surfaces maintain structural stability and precise force transfer without deformation.
Finally, the machine is used to test the durability and safety of the specialized surgical mallets and hammers themselves, verifying that the head-to-handle connection and the striking faces can withstand thousands of high-impact cycles without failure or material shedding.
Key machine capabilites
The machine offers several key advantages over manual testing:
- Precise, Repeated Impaction: The system delivers reproducible strikes with exceptional consistency in force and angle.
- Comparability Between Tests: Unlike manual methods, our automation ensures perfect data comparability across different instrument families, designs, and production runs, allowing for reliable validation and quality assurance.
- High Impaction Energies: Capable of generating up to 130 J of energy, the machine fully encompasses and surpasses the force levels observed in clinical practice, enabling rigorous validation for the heaviest surgical mallets and largest instruments.
- Failure Analysis with High-Speed Camera: Test can be captured using high-speed camera footage to provide detailed, frame-by-frame analysis. This allows you to pinpoint the exact moment and mechanism of failure (e.g., brittle fracture initiation, deformation, or bond separation), offering valuable insight for product development and quality control.
This technology provides data required to meet the functional validation requirements of standards like ISO 16061, ensuring your impaction instruments are safe and durable.
Typical Testing Parameters
Although a test protocol need to be tailored to each instrument, it can be helpful to have an example. Here are typical testing parameters fo a total hip replacement Cup Impactor:
| Parameter | Specification | Rationale |
| Impaction Energy | 2 J – 10 J (Adjustable range) | Simulates typical surgical mallet forces during hip surgery. |
| Test Cycles / Lifetime | 2,000 – 5,000 Impactions | Represents a 10-year service life for cumulative impact stress. |
| Instrument Samples | 3 samples per instrument design. | Allows an average to be calculated. |
| Implant Attachment | Worst-case implant (usually highest stiffness). | Maximizes the reaction force transmitted back to the instrument. |
| Bone Model | PU Foam Model (ASTM F1839 equivalent density). | Standardized support accurately mimicking cancellous bone damping. |
| Analysis Method | High-speed camera footage, functional evaluation before and after the test. | Pinpoints exact failure modes (fracture, deformation) for design insight. |