ISO 14243-1: Implants for surgery – Wear of total knee joint prostheses
Part 1: Loading and displacement parameters for wear-testing machines with load control and corresponding environmental conditions for tests.
ISO 14243-2: Implants for surgery – Wear of total knee joint prostheses Part 2: Methods of measurement.
ISO 14243-3: Implants for surgery – Wear of total knee joint prostheses, Part 3: Loading and displacement parameters for wear testing machines with displacement control and corresponding environmental conditions for test.
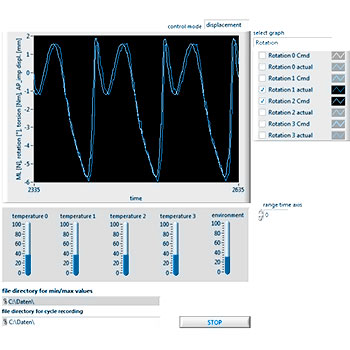
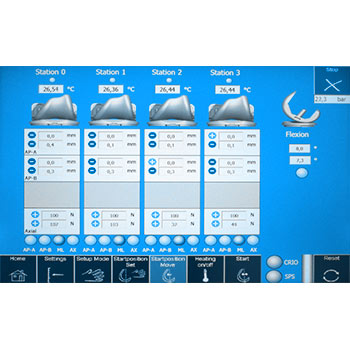
Wear of total knee endoprostheses as well as the implant kinematics can be determined using a total knee simulator. EndoLab® has developed a simulator that allows either a testing in force control (ISO 14243-1) or in displacement control (ISO 14243-3). Due to the servohydraulic actuators, excellent machine accuracy has been reached. Please refer the support section to see the simulator moving. Simultaneous testing of three (plus soak control) specimens enables rapid and economic developments. Routine testing is performed using calf serum as a test fluid. In general, the test is stopped after 5 million cycles. Wear is determined by weight loss and/or geometric measurements.
To see the simulator moving watch the video down below .
The wear of the components is determined gravimetrically, particle analysis can be performed. Calf serum with a protein content of 20 g/l is used for the tests.
This test is often combined with preconditioning according to ASTM F2003, analysis of the wear debris according to ISO 17853 as well as ion concentration analysis.
You are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More InformationYou are currently viewing a placeholder content from YouTube. To access the actual content, click the button below. Please note that doing so will share data with third-party providers.
More Information